 |
| In the photopupillary relfex test, the first photo is right after Alyssa removed her hand from her eye, and the second photo is a few seconds after her eye had adjusted to the intense light. |
Cayla Z: Anatomy and Physiology
This blog will be my journey through the class of Anatomy and Physiology.
Saturday, May 14, 2016
Reflex Lab
Wednesday, May 4, 2016
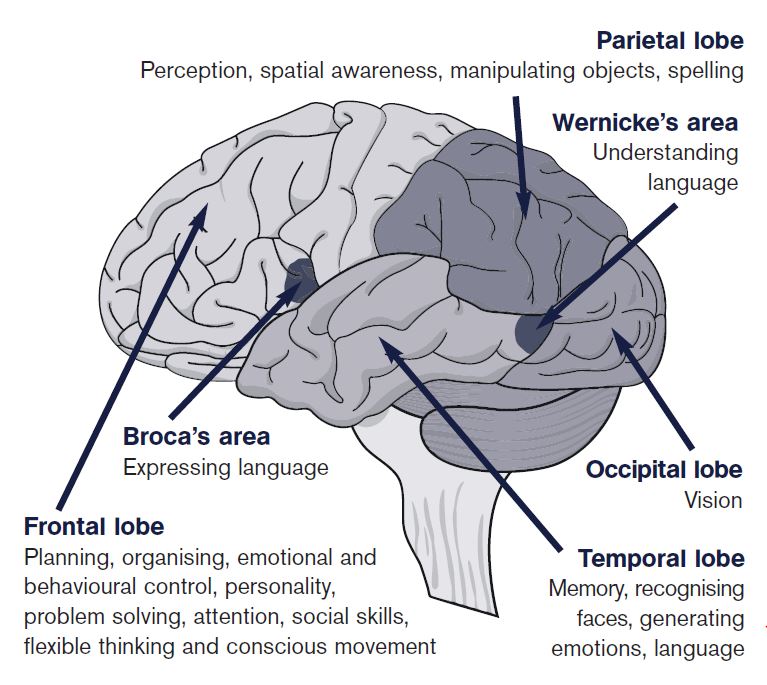
Brain Map
An interactive infographic by Open Colleges
Cerebral Cortex
1.
What do the frontal
lobes do? The frontal lobe is the "central command center" of the brain and controls an individuals personality, problem solving, memory, language, and impulse control. This part of the brain deals with executing and individuals behavior.
2.
What is the relationship between selective
attention and learning? The intelligence of an individual depends on how selective one is when remembering information. This is called selective attention, and it makes an individuals working memory capacity greater as it organizes important, unimportant, and little used information.
3.
What is the last part of your brain to develop
and what can you do to prevent it from deteriorating? The last part of the brain to develop is the frontal lobe, and is the first to deteriorate with age. However, there are two main ways an individual can do to prevent deterioration, including not "zoning out" where an individual needs to be engaged in his or her environment and returning focus to the five senses. Another exercise would be to transforming information, rather than memorizing it, brain function is about more than having a "good memory". Instead, it is about being able to take the information and create bigger ideas.
4.
What does the neo cortex do? The neo cortex has control over an individuals senses, spatial awareness, and motor skills.
5. What is the role of the pre frontal cortex? The main function of the pre frontal cortex is organizing thoughts and actions to match cohesively with internal goals.
6.
What do we know about the pre frontal cortex’s
relationship with multitasking? Despite what most people believe, multi-tasking does not exist. Instead, an individuals brain jumps from one task to another quickly, often leading to inferior quality of the tasks being performed.
7.
Which part of the brain is associated with
speech and language development? Give an
interesting fact about this region. The Broca's area is associated with speech and language development. In studying this area of the brain, it has been showed that tongue twisters often improve the functioning of the Broca's area.
8.
Which part of your brain is responsible for
thinking the following: “Is it hot in here or is it just me?” The somatosensory cortex is the part of the brain that responds to touch, as well as senses pain and pleasure. This part of the brain also interprets temperature.
9.
What does your visual cortex do for
you? The visual cortex is a part of the brain that helps differentiate between colors and distinguishing complex items, such as faces. Without this lobe, every individual would appear the same.
10. State
three interesting or significant facts about your occipital lobe. Within the occipital lobe, there are different regions that focus on various jobs, such as sensing motion, differentiating colors, and spatial processing. If this lobe is damaged, it could result in partial or total blindness, difficulty differentiating colors, and hallucinations. In addition, this part of the brain participates in an individuals imagination and allows one to process short and long time memories.
11. What
would happen if your temporal lobes were damaged? The temporal lobe helps keep the visual memories in the brain, comprehending language, processing emotions and what they mean, new memories, and newly learned information. Without this portion of the brain, an individual loses all potential of long term memory.
12. What
is your “fast brain” and what does it do? The "fast brain", also called the eye fields, control eye movements and helps the brain quickly register information. This area of the brain can pick up information in milliseconds, which is faster than any other part of an individual's brain.
Neuron
13. State
3 things that you could do that would influence your synapses, and have a positive affect on your life and health. Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise can have a great impact on an individuals brain health and function. Studies have found that omega fatty acids, such as salmon, can have a positive effect on an individuals synapses. In addition, studies indicate that socializing can also have an effect on the function of the brain.
14. What
is the relationship between multi-sensory or multi-modal learning and your dendrites? Studies have shown that an individual needs "big picture" thinking in order to fully understand a subject, and then break that subject down into relevant parts. The learning should be structured around the real problems in order to put the learner into the context of what is being learned.
15. How
does “big picture thinking” and mnemonics affect dendrites and/or learning? As an individual learns things, the number of dendrites in his or her brain grows. On the other hand, the unused synapses die and the ones that are commonly used are strengthened. This means, that practicing a certain task a lot, strengthens the pathways used.
16. Describe
a neurotransmitter that you feel is
very important. Justify your reasoning. An important neurotransmitter that is important would be dopamine, released from the brain when an experience is enjoyable and travels from neuron to neuron in tiny electrical currents. This neurotransmitter is important because it is a "reward" for your brain for learning new information or trying new experiences. Without dopamine, an individual would not be motivated to try new things or learning, dopamine provides an incentive for one's brain to retain new information.
Limbic System
17. What
does the corpus callosum do? The corpus callosum is a band of nerve fibers that allows for the communication between the two hemispheres of the brain. The corpus callosum is where the oral language skills and the ability to comprehend language is found.
18. What
is the relationship between music and the corpus
callosum? Studies have shown that studying music can help an individual strengthen the "conversation" between both sides of the brain, however, for this effect to last, the individual must practice often.
19. Why
is the thalamus important? The thalamus is important due to the fact that it controls the motor control, sensory information, and states of consciousness. It is also important because it retrieves memories and processes information.
Relate and Review
Summarize what you
learned from this tutorial. Relate what
you learned to your everyday life and how you can make it better. Use at least 5 of the bolded words from the
questions. 5-sentence minimum. You may
use the back of this if needed.
In this tutorial, it mainly focused on the important structures of the brain, its functions, and its effects on the individual. The frontal lobe is the "central command center" of the brain and controls an individuals personality, problem solving, memory, language, and impulse control. This part of the brain deals with executing and individuals behavior. The three cortex's: the neo cortex, pre frontal cortex, and the visual cortex all have varying functions. First, the neo cortex has control over an individuals senses, spatial awareness, and motor skills; the pre frontal cortex is organizing thoughts and actions to match cohesively with internal goals; and the visual cortex is a part of the brain that helps differentiate between colors and distinguishing complex items, such as faces. Without this cortex, every individual would appear the same. Within the occipital lobe, there are different regions that focus on various jobs, such as sensing motion, differentiating colors, and spatial processing. If this lobe is damaged, it could result in partial or total blindness, difficulty differentiating colors, and hallucinations. In addition, this part of the brain participates in an individuals imagination and allows one to process short and long time memories. The temporal lobe helps keep the visual memories in the brain, comprehending language, processing emotions and what they mean, new memories, and newly learned information. Without this portion of the brain, an individual loses all potential of long term memory. Taking the relationship between dendrites and the most effective way of learning, studies have shown that an individual needs "big picture" thinking in order to fully understand a subject, and then break that subject down into relevant parts. The learning should be structured around the real problems in order to put the learner into the context of what is being learned. An important neurotransmitter that is important would be dopamine, released from the brain when an experience is enjoyable and travels from neuron to neuron in tiny electrical currents. This neurotransmitter is important because it is a "reward" for your brain for learning new information or trying new experiences. Without dopamine, an individual would not be motivated to try new things or learning, dopamine provides an incentive for one's brain to retain new information. The corpus callosum is a band of nerve fibers that allows for the communication between the two hemispheres of the brain. The corpus callosum is where the oral language skills and the ability to comprehend language is found. The thalamus is important due to the fact that it controls the motor control, sensory information, and states of consciousness. It is also important because it retrieves memories and processes information.
In order to improve an individuals everyday life, maintaining a healthy diet and exercise can have a great impact on an individuals brain health and function. Studies have found that omega fatty acids, such as salmon, can have a positive effect on an individuals synapses. In addition, studies indicate that socializing can also have an effect on the function of the brain.
Sunday, May 1, 2016
Sheep Brain Dissection


 In this dissection, we were able to identify the main structures of the brain and their functions as well as the ability to practice proper dissection techniques. In different stages of the dissection we were able to see the outer and inner structures of the brain, including: the cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem, corupus collosum, medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, thalamus, and hypothalamus. Using what we had learned in our notes, we were able to determine the functions of each of the structures we identified. Before we began to dissect, we identified various structures which included the cerebrum in the brain provides for higher brain functions such as thoughts or actions. As for the cerebellum, it coordinates and regulates muscular activity. The brain stem transports information to and from the brain. The main function of myelin in a neuron is to increase the speed of nerve impulses. As we cut the brain longitudinally, in the pictures above, it contains the corpus collosum, the medulla oblongata, pons, the midbrain, thalamus, and the hypothalamus. The main function of the corpus collosum is a large bundle of neuron fibers that connect the two hemispheres of the brain. The medulla oblongata main function is aiding in digestion, the pons helps in circulation, and the midbrains main function is to help with breathing. The optic nerve main purpose is to transfers visual information from the retina to the visual centers of the brain from electrical impulses. Lastly, the thalamus' main function is sorting data and sending it to its desired location and the hypothalamus' main function is maintaining homeostasis.
In this dissection, we were able to identify the main structures of the brain and their functions as well as the ability to practice proper dissection techniques. In different stages of the dissection we were able to see the outer and inner structures of the brain, including: the cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem, corupus collosum, medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, thalamus, and hypothalamus. Using what we had learned in our notes, we were able to determine the functions of each of the structures we identified. Before we began to dissect, we identified various structures which included the cerebrum in the brain provides for higher brain functions such as thoughts or actions. As for the cerebellum, it coordinates and regulates muscular activity. The brain stem transports information to and from the brain. The main function of myelin in a neuron is to increase the speed of nerve impulses. As we cut the brain longitudinally, in the pictures above, it contains the corpus collosum, the medulla oblongata, pons, the midbrain, thalamus, and the hypothalamus. The main function of the corpus collosum is a large bundle of neuron fibers that connect the two hemispheres of the brain. The medulla oblongata main function is aiding in digestion, the pons helps in circulation, and the midbrains main function is to help with breathing. The optic nerve main purpose is to transfers visual information from the retina to the visual centers of the brain from electrical impulses. Lastly, the thalamus' main function is sorting data and sending it to its desired location and the hypothalamus' main function is maintaining homeostasis.

Wednesday, April 27, 2016
Sheep Eye Dissection Analysis
 |

After cutting the eye along the sclera, we got a view of the retina- receives light and converts the light into neural signals- which lines the posterior side of the eye. Inside of the eye contains a transparent fluid, vitreous humor, fills the cavity of the eye. This fluid, along with the aqueous humor, help in maintaining the shape of the eye.



After removing the vitreous humor, the lens was then revealed as well as the ciliary body and the suspensory ligament. A lens is held in place by the suspensory ligament that join with the smooth muscle, that contains the ciliary body. When the smooth muscle fibers contract, it causes the lens to flatten and the degree of bending light, as a result, is reduced.

Then, we removed the lens and were able to see light coming through a oval shaped transparent opening, known as the pupil, found in the center of the iris. In contrast to a circular pupil, the sheep's pupil is oval shaped. In the second cavity between the iris and the cornea, is filled with a fluid called aqueous humor.
Thursday, April 14, 2016
Clay Brain
For this activity, we build a two dimensional brain out of play dough and labeled specific parts. The larger brain represents the inside view with the brain stem, cerebrum, corpus colossum, cerebellum, and the thalamus. In the smaller brain, we showed the outer portion of the brain which also represented the lobes, such as the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe.


Wednesday, April 13, 2016
"The Woman With The Hole In Her Brain"
In the article "The Woman With The Hole In Her Brain", describes a woman who upon receiving a CAT scan discovered that a small part of her brain- the cerebellum- was missing. In the space where her cerebellum should be, was cerebrospinal fluid- which provides defense for the brain against disease. The cerebellum represents ten percent of the brains total volume; however, makes up fifty percent of its neurons. The main function of the cerebellum is controlling voluntary movements and balance, and possibly involved in the ability for a individual's motor actions and speech. Without a cerebellum, many possible complications could arise such as mental impairment, epilepsy, or a build up of fluid in the brain. The woman, however only seemed to suffer from mild speech problems and mild motor deficiency.
The frontal lobe is considered the emotional control center and the "home" of an individuals personality. It is also involved in motor function, problem solving, memory, language, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior. The frontal lobe is very vulnerable due to the fact that it is located in the front of the skull and its large size. If a individual injures his/her frontal lobe, it can effect the personality of the individual, as well as difficulty interpreting feedback from the environment, and difficulty with different facial expressions and problem solving. Even though the damage to the frontal lobe can be permanent, rehabilitation is possible to regain a small degree of prior function.
 |
| Frontal Lobe Damage |
The frontal lobe is considered the emotional control center and the "home" of an individuals personality. It is also involved in motor function, problem solving, memory, language, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior. The frontal lobe is very vulnerable due to the fact that it is located in the front of the skull and its large size. If a individual injures his/her frontal lobe, it can effect the personality of the individual, as well as difficulty interpreting feedback from the environment, and difficulty with different facial expressions and problem solving. Even though the damage to the frontal lobe can be permanent, rehabilitation is possible to regain a small degree of prior function.
Thursday, March 24, 2016
Unit 7 Reflection
In this unit, we learned about the major muscles in the body, and in a chicken; how various muscles work in order to create a certain desired movement, the contraction and relaxation of muscles, and the affects of different types of performance enhancing drugs. In the beginning of this unit, we started out learning about the directional capabilities of the synovial joints ranging from abduction and adduction- the movement of limbs away and toward the body- to inversion and eversion- which turns the sole of the foot inward and outward.
Moving onto the muscular system, we learned about the properties of muscle tissue- which include contractability, the ability of the muscle to shorten when stimulated; extensibility, the ability to be stretched; and elasticity, which is the ability of the muscle to recoil to resting length. In classifying the muscles, there is the "prime mover" which causes a desired action, the antagonist which relaxes when the prime mover contracts, the synergist which assists the prime mover by reducing unnecessary movements, and the fixator which stabilizes the origin of the prime mover.
Then, we learned about how the muscle contracts and retracts. During contraction, the nerve sends an impulse to the muscle, and Ca+ ions are released into the sacroplasmic reticulum, the Ca+ binds to proteins around actin filaments, the binding of the Ca2+ causes myosin filaments to pull on the actin filaments, and the sarcomere is shortened. In relaxation, the impulse passes, the Ca2+ gate closes, and the Ca2+ is transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. In order to demonstrate this process and how muscles work, we created a short video describing this.

 Learning about the major muscles of the body made it easier to recognize the similar muscles during the dissection. In the chicken dissection , we were able to discover the pectoralis major, the pectoralis minor, that allows the chicken to close and open its wings; the gluteus maximus, and the hamstring group. When comparing the major muscles of the chicken to the major muscles of the human, many of the muscles were similar and helped complete the same desired actions.
Learning about the major muscles of the body made it easier to recognize the similar muscles during the dissection. In the chicken dissection , we were able to discover the pectoralis major, the pectoralis minor, that allows the chicken to close and open its wings; the gluteus maximus, and the hamstring group. When comparing the major muscles of the chicken to the major muscles of the human, many of the muscles were similar and helped complete the same desired actions.
Next, we learned about the three different muscle fiber types: slow twitch, fast twitch A, and fast twitch B. With slow twitch muscle fibers, they are best suited for long duration due to their slow contractability and high amounts of myoglobin. Both fast twitch A and B are better suited for shorter duration, as they have fast contractability and high glycogen storage. In order to keep the muscles strong and healthy, exercising and eating healthy are required. Fast twitch muscles are improved by brief and intense workouts, and slow twitch fibers can be improved by cardiovascular training.

Lastly, we learned about the causes and effects of using performance enhancing drugs. Many individuals begin the use of performance enhancing drugs due to the pressures from peers, role models, media influences, and self body image. Specific effects of using performance enhancing drugs are severe and negative as it can cause high blood pressure, liver damage or cancer, or blood clots and stroke.
If there are so many detrimental effects to the use of performance enhancing drugs, why do individuals still continue to take the risks? Throughout this school year, I feel as though I have grown into a better student and have become more concentrated on living a healthier lifestyle. With my New Year's goals, I am slowly making progress and focusing more on managing my stress and sleep levels as I realized the effects it was having on my body- making me constantly tired throughout the day.
Moving onto the muscular system, we learned about the properties of muscle tissue- which include contractability, the ability of the muscle to shorten when stimulated; extensibility, the ability to be stretched; and elasticity, which is the ability of the muscle to recoil to resting length. In classifying the muscles, there is the "prime mover" which causes a desired action, the antagonist which relaxes when the prime mover contracts, the synergist which assists the prime mover by reducing unnecessary movements, and the fixator which stabilizes the origin of the prime mover.
Then, we learned about how the muscle contracts and retracts. During contraction, the nerve sends an impulse to the muscle, and Ca+ ions are released into the sacroplasmic reticulum, the Ca+ binds to proteins around actin filaments, the binding of the Ca2+ causes myosin filaments to pull on the actin filaments, and the sarcomere is shortened. In relaxation, the impulse passes, the Ca2+ gate closes, and the Ca2+ is transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. In order to demonstrate this process and how muscles work, we created a short video describing this.

 Learning about the major muscles of the body made it easier to recognize the similar muscles during the dissection. In the chicken dissection , we were able to discover the pectoralis major, the pectoralis minor, that allows the chicken to close and open its wings; the gluteus maximus, and the hamstring group. When comparing the major muscles of the chicken to the major muscles of the human, many of the muscles were similar and helped complete the same desired actions.
Learning about the major muscles of the body made it easier to recognize the similar muscles during the dissection. In the chicken dissection , we were able to discover the pectoralis major, the pectoralis minor, that allows the chicken to close and open its wings; the gluteus maximus, and the hamstring group. When comparing the major muscles of the chicken to the major muscles of the human, many of the muscles were similar and helped complete the same desired actions.Next, we learned about the three different muscle fiber types: slow twitch, fast twitch A, and fast twitch B. With slow twitch muscle fibers, they are best suited for long duration due to their slow contractability and high amounts of myoglobin. Both fast twitch A and B are better suited for shorter duration, as they have fast contractability and high glycogen storage. In order to keep the muscles strong and healthy, exercising and eating healthy are required. Fast twitch muscles are improved by brief and intense workouts, and slow twitch fibers can be improved by cardiovascular training.

Lastly, we learned about the causes and effects of using performance enhancing drugs. Many individuals begin the use of performance enhancing drugs due to the pressures from peers, role models, media influences, and self body image. Specific effects of using performance enhancing drugs are severe and negative as it can cause high blood pressure, liver damage or cancer, or blood clots and stroke.
If there are so many detrimental effects to the use of performance enhancing drugs, why do individuals still continue to take the risks? Throughout this school year, I feel as though I have grown into a better student and have become more concentrated on living a healthier lifestyle. With my New Year's goals, I am slowly making progress and focusing more on managing my stress and sleep levels as I realized the effects it was having on my body- making me constantly tired throughout the day.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

